ENDEE BUILDING ADDITIONS
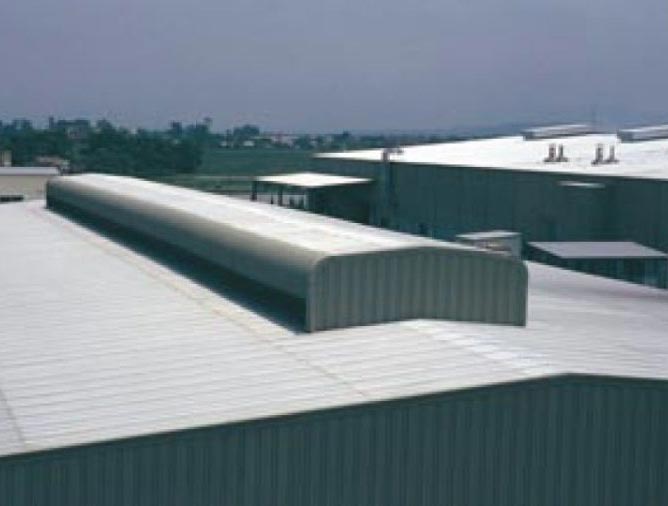
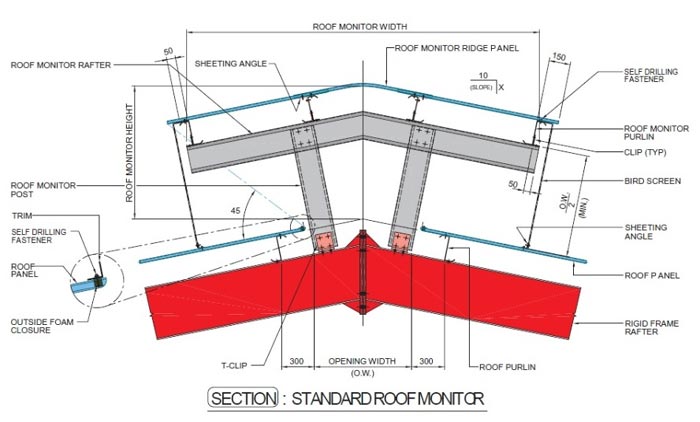
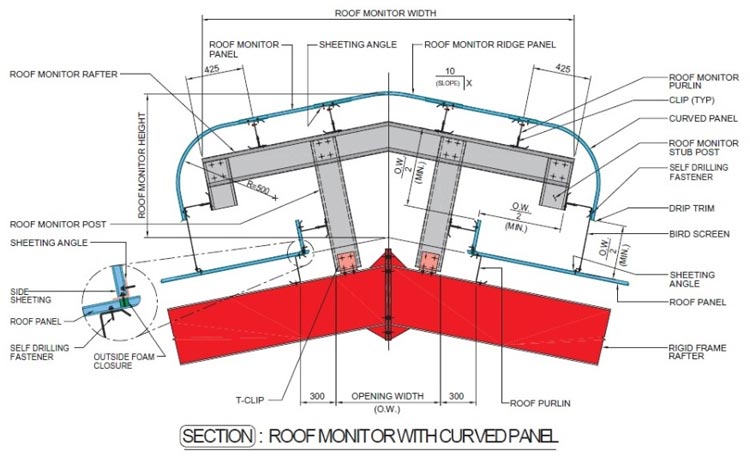
ROOF MONITOR
Roof monitor combines economy, good appearance and easy
erection. The size of the monitor can be adjusted to suit exact
ventilation and lighting requirements. The overhang part is
detailed to give a 45° protection from the rain. A light wire mesh is
installed at 45° to prevent intrusion of birds. A curved eave panel
may be incorporated at the eave of the monitor. It is very
conducive to tropical areas where rainfall is normally heavy.
Generally, roof monitors are made of lightweight, yet strong, coldformed
sections. Built-up sections and hot rolled sections are used
for the framing members when the roof monitor is large and design
warrants their use.
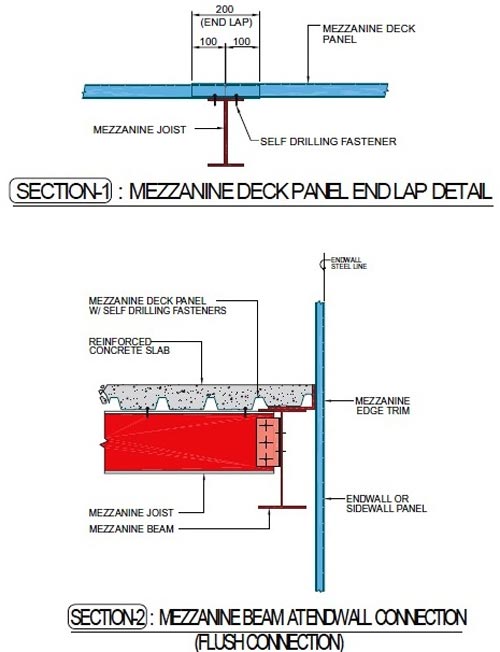
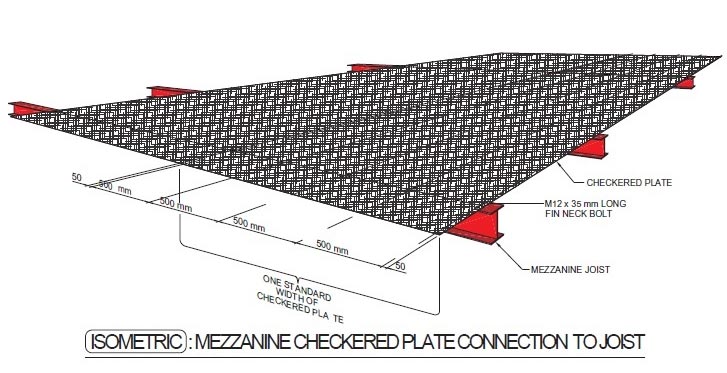
The mezzanine structures consists of built-up or hot rolled main mezzanine beams that support built-up, hot rolled or cold-formed mezzanine joists which, in turn, support a metal deck. A reinforced concrete slab is cast on the metal deck as the finished surface. The metal deck is not designed to carry the floor live loads; it is intended only to carry the reinforced concrete slab during pouring. The reinforced concrete slab must be designed to carry the floor loads.
MEZZANINE
A mezzanine is an elevated flooring system located inside the outer shell of a pre-engineered steel building. The most common uses of a mezzanine are to accommodate offices or to serve as a storage area. Generally, the mezzanine framing is connected to the main rigid frame columns for lateral stability. Primary and secondary mezzanine members are analyzed as pinned at both ends. Though this design approach may result in a slightly heavier design, it has proven to be safer in the long term due to the possibility that the mezzanine may be partially removed as building layouts change during the lifetime of a structure.The mezzanine structures consists of built-up or hot rolled main mezzanine beams that support built-up, hot rolled or cold-formed mezzanine joists which, in turn, support a metal deck. A reinforced concrete slab is cast on the metal deck as the finished surface. The metal deck is not designed to carry the floor live loads; it is intended only to carry the reinforced concrete slab during pouring. The reinforced concrete slab must be designed to carry the floor loads.